
Hiring Staff
Chapter 1: The hiring process: how to hire staff
Are you prepared to bring on board your very first worker? Or, perhaps you already have a small number of employees but would like to enhance the hiring process in order to identify more qualified candidates. Congratulations, this is an important step in the development of your rapidly expanding business!
However, before you get started, you need to be sure that you have a complete understanding of the steps involved in the recruitment process. There is a great deal more to it than simply job descriptions, interviews, contracts, and payments. When you hire people, you should focus on selecting good employees, getting the most out of your team, and being aware of the obligations that come with being an employer.
The hiring process in a nutshell
The process of hiring new employees is exciting, but due to the large number of processes involved, it may also be extremely overwhelming. This tutorial will walk you through the process step by step so that you may identify people who are a perfect fit for your company.
First, create a hiring strategy
When you hire your first employee now and continue to develop your team in the future, having a well defined hiring strategy can help set your company up for success and pave the way for continued expansion. Your hiring strategy should provide you with a clear knowledge of your employment requirements as well as how to meet those requirements. It is a strategy that guides you through the many stages of the recruitment process and helps you succeed.
When developing your approach to the hiring process, the following are three questions that are necessary to ask:
- Who do you need?
Make a selection based on the kind of employee your company need. It may be someone to fill in the gaps in your expertise, someone to do the things you could if you had more time, or someone to do the things you don’t love doing. Any one of these options is possible, as well as a combination of several of them. This provides you with a strong understanding of the abilities, experience, and other qualifications that should be sought for in a potential employee.
After determining the type of individual you require, the next step is to strike a balance between the attitude and talents desired in that individual. It is possible that it will be simpler for you to teach a diligent worker the talents you require rather than hiring someone who already possesses all of the necessary skills but lacks the go-getter attitude that you are looking for. - What type of employee do I need to hire?
Determine the type of worker who would be most beneficial to your company. Every type of worker, whether they are independent contractors, employees, or those who work either part-time or full-time, has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Do your research to determine which option is most suitable for your company. - What can you afford?
Before you go out and look for a job, you need first do some planning for your finances. Find out what the going rate is in your field so you can offer a pay that is not only competitive but also fits within your financial constraints. Other costs that need to be taken into consideration include employer contributions to superannuation, any bonuses or incentives that you want to offer employees, advertising fees for job posts, and even more charges. Make a plan for your budget based on these costs to determine what you are able to purchase. Make use of the pay calculator provided by the Fair Work Ombudsman to obtain an idea of how much it could cost to bring on a new worker.
Payroll is a big financial commitment.
Finding the money to pay staff frequently requires the individual to make sacrifices of their own.
50% of employers have chosen not to take wage increases or bonuses for themselves in order to provide them to their employees.
40% of employers have made payments to employees out of their own personal funds at some point in the past.
Chapter 2: Make it official – register as an employer
After you’ve developed a plan for recruiting new employees, it’s time to sign up as a business that hires people. Since this could take some time, you should get the procedure started as soon as possible.
The following is what you need to do:
- In order to register for pay as you go (PAYG) withholding tax, you will need to have an ABN number.
- If you intend to hire workers who hold either a working holiday visa or a work and holiday visa, you will also be required to register as an employer of working holidaymakers. This registration is mandatory.
- You can register either online, over the phone, or through your registered tax agent. For additional information, check the ATO sites on PAYG withholding and employer registration for working holidaymakers. You can register either online, over the phone, or through your registered tax agent.
Understand employment law
Before you start recruiting, you should familiarise yourself with the applicable legislation because they regulate the entire employment process.
If you are interested in learning more about employment regulations and how to comply with them, you should consult with an employment lawyer for specialised assistance or check out a government website.
On the website of the Fair Work Ombudsman, visitors can get useful fact sheets and guidelines on the best practices regarding workplace rules.
Chapter 3: Write a job description and promote it
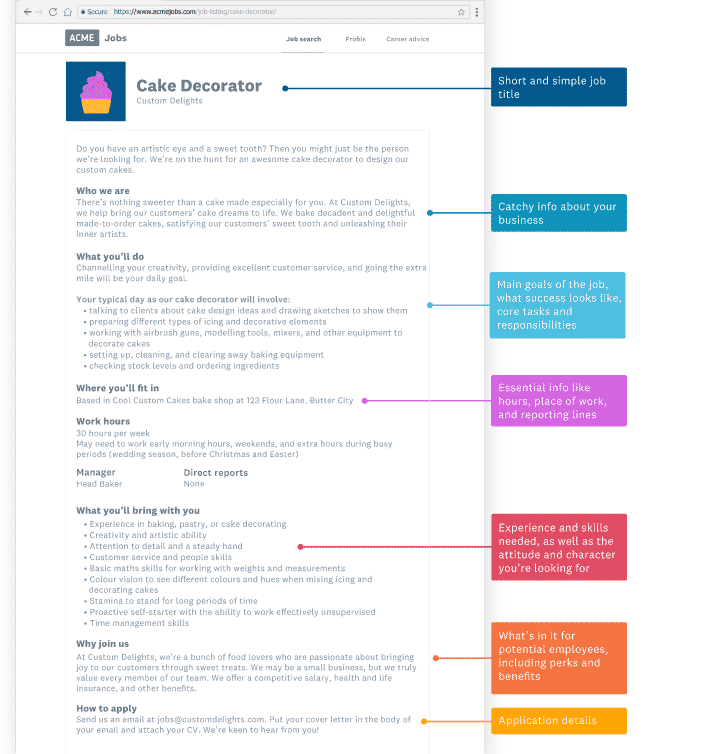
(Credit: Xero.com)
Have you been tasked with writing a job description? We will provide you with ideas on how to advertise your job vacancy and show you how to get the most qualified applicants to apply for the position.
Hiring is a lot like matchmaking. You’re seeking for the perfect employee, but candidates for jobs are also searching for the ideal employer, role, and environment for them to do their work in. You need to compose a job description that is distinct from the others in order to attract the attention of the ideal candidate.
Anatomy of a job description
Let’s pretend there’s a bakery called Custom Delights that bakes cakes to order and caters to all kinds of events and celebrations. Because the company is expanding, they have made the decision to employ a cake decorator to assist them in the process of designing their cakes.
You should give some thought to creating a separate email account specifically for the purpose of submitting job applications. This will ensure that your applications are not confused with other, more important communications. In addition to this, it makes it simpler for you to organise applications in the future.
Make your job description inclusive
When you are writing the job description, make sure to include everyone. Make sure you choose your words carefully so that you don’t run the risk of offending someone or breaking any laws about diversity or equality. Consider the accessibility of facilities for those with various health problems and/or disabilities. Think about methods to provide accommodations for persons who are caring for a kid, an ill or elderly family member, or another person in a situation that is analogous to their own.
Visit the page on equal opportunity and diversity at business.gov.au for additional details, as well as the page on preventing discrimination in recruiting located at the Australian Human Rights Commission’s website.
Ten ideas to promote your job description
It’s time to let everyone know about your fantastic job description now that you’ve finished writing it. Spread the word by utilising one of the following strategies:
- Your website
You should publish the complete job description on your website in a location that is intuitive and simple to locate. - Referrals from existing employees, business partners, or clients
Ask your current employees, business partners, or customers if they know anyone who could be a good candidate for the job, and see if they can provide any names. It would be even more advantageous if they had previously collaborated with the applicants; in that case, they would be able to offer insights based on the experiences they have gained, and candidates might also come highly recommended. - Your company’s social media accounts
You should update all of your company’s social media accounts with a condensed and interesting version of the job description, along with a link to the complete version of the description. - Your personal social media accounts
It’s possible that a member of your family or a buddy of a friend already exists in your social network who is qualified for the job you’re looking for. You should publish an advertisement that is comparable to what you’ve published on the social media accounts associated with your company, but you should add a personal touch to it. Only consider this alternative if you are confident in your ability to hire close relatives or friends and then fire them if things don’t go as planned. You will need to keep your personal relationship with them separate from the professional one, and you should treat them the same way you would treat any other employee. - Trade and industry associations
If the position you are hiring for is specialised to an industry or requires certain trades or abilities, you should advertise it in industry journals, trade magazines, or on the websites of association organisations. - Local community groups or business organisations
It can be an effective method for recruiting top local talent to post job openings on the message boards of local community groups or on the websites of local business organisations. - Local government agencies
Collaborate with a local government agency that is dedicated to assisting job seekers who are currently unemployed. You can advise them of your openings, and they will be able to aid you in locating candidates that are a good fit for the position. - Universities
Posting jobs on job boards maintained by universities and alumni associations is a good strategy to take if you need candidates with particular degrees or qualifications. - Job boards
It is common practice for job boards to charge fees; but, if you are having problems locating qualified candidates using any of the alternatives described in the previous paragraphs, it may be worthwhile to investigate using job boards. There is a large number of applications, and sorting through all of them takes some time. - Recruitment agencies
The use of recruitment agencies is an even more expensive alternative to using job boards. However, if you have the financial resources available, it may be more productive to outsource the process of recruitment to agencies or recruiters.
Chapter 4: The selection process – from interview to job offer
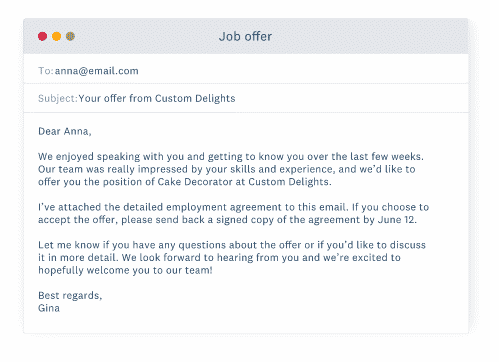
(Credit: Xero.com)
Identifying the most qualified applicant is a challenging task. In order to write up a job offer letter for you, we put you through the selection process and conduct interviews.
It appears that you have been successful in attracting a number of individuals who are interested in finding employment opportunities due to the number of applications that have been submitted. But how are you supposed to sift through all of them and pick out the absolute best ones?
Create a cream-of-the-crop shortlist
The most difficult and time-consuming element of the hiring process is frequently the stage in which recruiters must read through applications and choose potential applicants for further consideration. The following is what you need to do:
- Settle on a number for your shortlist
Find a number that makes you feel comfortable, and put a few candidates in a separate pile labelled “maybe” in case the original shortlist you’ve chosen doesn’t work out. - Create a set of criteria based on your job description
Make a list of the essential qualifications for the position. Create a second list of desirable but not required characteristics, which might serve as a deciding factor amongst candidates who are equally qualified in terms of their experience or talents. - Filter candidates
Choose candidates that meet (nearly) all of the requirements for the necessities, and also make sure to look for any desirable extras that will give them an advantage over the other applicants. - Deliver the news
Share the good news with those individuals who have been chosen for further consideration in the recruitment process, and let them know what comes next. Send a word of appreciation to individuals who were not chosen for the position, and offer your best wishes to them as they continue their quest for employment.
Interviews: the getting-to-know-you stage
Now that you have a potential shortlist of candidates, it is time to narrow it down through the interview, which is the most exciting aspect of the process of hiring new employees. This is the stage in which you learn more about your potential employees, and it is also the stage on which your possible employees discover more about you.
Before the interview
Make a decision regarding each of the following before beginning the interview:
- how many interviews you’ll have
- how much time do you need for each interview
- the types of interviews you’ll be doing
- the questions you’ll ask for each interview
During the course of the interview, there are certain things that you are not permitted to ask, do, or say. If you are unsure, seek the counsel of an employment lawyer, read the rules on how to avoid discrimination, and familiarise yourself with any privacy regulations that you are required to be aware of. Check out the Fair Work Ombudsman’s page dedicated to privacy in the workplace.
Types of interviews
Choose the type of interview that best suits the requirements of your job. It can be one or a combination of the following:
- Phone interviews or video calls
These kinds of interviews work well for people who are working remotely or who are unable to attend in person due to factors such as extended travel durations, the need for childcare, or some other condition. During the preliminary screening of candidates, it is common practice to conduct brief phone interviews to obtain a sense of how the individual would fit into the role. - In-person interviews
These interviews can be conducted one-on-one or with multiple interviewers at the same time. In order to gain a second or third opinion, you should bring in anyone else the candidate would be working with, such as a manager or a coworker, for example. They have the ability to validate your findings, point out anything you may have overlooked, or even show you that you are mistaken. However, you should be careful not to bring in too many individuals in order to prevent overloading your prospect. The optimal number of interviewers for each interview is typically two persons. Convention dictates that face-to-face interviews take place in conference rooms, so why not shake things up and try something new? Candidates can be shown about your workplace, introduced to members of your team, and evaluated based on how well they get along with others and have an interest in your company. You can also learn more about a candidate’s personality by seeing them in a setting that is less formal and more relaxed. For example, you could take them out for coffee. - Skills-based assessments
You can demonstrate that you have the abilities that are necessary for your job by taking examinations that are based on those skills. It may take the form of an interview in which candidates are asked a number of technical questions, a written examination, a test project, or a series of brief activities carried out in a working environment. Be sure that the evaluations don’t take up too much time and that they focus solely on a candidate’s ability to perform the essential duties of the position.
Be fair and consistent in your interviewing methods, regardless of which ones you use. Make it a point to ask all of the candidates identical questions and to approach them all in the same way. Make an effort to keep interviews casual, and don’t drag them out for any longer than necessary; an hour or so should be sufficient.
Questions to ask during the interview
When conducting interviews, in order to select the most qualified candidate for a position, it is important to ask a variety of questions that can assist assess whether or not a candidate is a good fit. Instead of asking them yes-or-no questions, you should ask them open-ended inquiries to encourage conversation.
While there will be certain questions that are unique to the position, a person’s profession, or their previous work experiences, there will also be some questions that are universal in nature and can be asked to anyone who is being interviewed. The following are some questions that are appropriate to ask potential applicants during interviews:
At the end of the interview, it is appropriate to express gratitude to the interviewees for their participation. Inform them when they may expect to hear back from you as well as the following steps that will be taken.
Make an offer they can’t refuse
The time for frivolity and distraction is passed; now it’s time to get down to serious business.
Make your decision based on all of the material you have obtained, including the cover letters, CVs or resumes, and notes from the interviews.
You should schedule a meeting with other members of your team who are interviewers as soon as possible following an interview to discuss their impressions of the candidate.
Top tips for selecting a candidate
The following are three considerations that will assist you in making your choice of candidate:
- When making your selections, you should strive to be as fair and impartial as you possibly can.
- By advocating for diversity, you can challenge any implicit or unconscious biases you might have. Having access to a variety of points of view not only fosters creativity and invention but also assists in the process of determining which solution is the most effective.
- If you find yourself unable to make a choice, it is important to have faith in your gut feelings and act in accordance with those.
Before making an offer
Before making an offer, it is essential to check the references of the potential tenant.
Referees are people who can provide feedback to you about a candidate’s previous performance and help you decide whether or not to hire them. Request permission to contact the candidates’ references and ask the candidate you’ve chosen to provide at least two references.
It’s helpful to have references in writing, but it’s even more beneficial to talk to referees over the phone. Put them through a series of tests that can verify a candidate’s character or skills.
In the event that your top candidate’s referees don’t provide positive feedback or your prefered candidate doesn’t accept your terms and conditions of employment, it is time to draught an employment agreement.
Reference checks on your second and third choices will allow you to make an offer to those candidates in the event that your top candidate’s referees don’t provide positive feedback. An employment agreement is a written contract that outlines the terms and conditions of employment, and it is signed by both the employer and the employee.
What to include in an employment agreement
Employment agreements must include the following information:
- employer name
- employee name
- job description
- hours and place of work
- pay
- whether employment is casual, fixed-term, full-time, part-time, or permanent
- start date (and end date for fixed-term employment)
- entitlements such as leave and holidays, holiday work pay, and more
Other terms of employment included in the agreement are the benefits to which the employee is entitled, the process by which issues arising from the employment relationship will be resolved, the notice periods to be observed when terminating employment, the trial or probation periods, the provisions governing what occurs in the event that the business is restructured or sold, and the confidentiality clauses.
Seek the counsel of an attorney whenever you have questions about whether or not the provisions of your employment agreement are legal and whether or not they comply with all applicable employment and labour regulations.
You can write your own letter of engagement with the help of a template that can be found on the website of the Fair Work Ombudsman.
Make a formal offer
After you have finished drafting the agreement, it is time to make the job offer to the candidate that you have selected.
Give them sufficient time to think about your offer and obtain an independent opinion regarding the agreement, and make sure they are aware of when you will require a decision from them.
It is possible that the candidate you have chosen will not immediately accept the offer you have made, so you should be prepared to answer any questions they may have and negotiate any terms they choose. After you and the potential employee have reached a consensus on the alterations, the employment agreement needs to be signed by both of you. You should give a copy of the signed agreement to the employee, and you should also keep a copy of it for your own records.
Chapter 5: Check your employer’s responsibilities
When you have excellent workers, you also have enormous obligations. Find out more about the duties that come with being an employer and how to fulfil them.
Check your employer’s responsibilities
Congratulations on this momentous turning point for your company, which was the hiring of your new employee. It is an exciting time when you recruit your first team member or add a new person to your expanding group of workers. It is possible that you may have some time before your new employee starts, so take advantage of this window of opportunity to review your duties as an employer and ensure that you are well prepared.
Always act in good faith and treat employees fairly.
When dealing with staff members, it is imperative that all actions be carried out in good faith. Always maintain your honesty and adhere to a procedure that is fair.
Give your staff the opportunity to voice their issues, and respond to those concerns as soon as possible. If you have a problem with one of your employees, you should talk to that person about it as quickly as possible and clear up any confusion that may exist.
Pay employees on time
Paying employees according to the rate that is outlined in the employment contract is one of the responsibilities that come with being an employer. Pay them using the form of payment that was agreed upon, and pay them on the day and at the frequency that is specified in the agreement. Make sure that you present your employees with pay stubs that detail any deductions or contributions that have been made from their paychecks.
Besides your legal responsibilities, payroll is also personal. It’s not uncommon for employees to have a lot riding on the outcome.
63% have financial difficulties before payday*
33% have less than $100 left by payday*
* Xero Australian workforce survey, 2019
Deduct the correct amounts
One of the things that gets subtracted from an employee’s salary or compensation is the amount that they owe in income tax. Make sure that you are taking out the appropriate amount from each employee’s paycheck by basing it on how much they make.
Other payments, such as allowances or bonuses, may be subject to taxation; therefore, it is imperative that you deduct the appropriate amount for these types of payments. Check to see if there are any other deductions that need to be made for each pay period as well.
Investing in online payroll software that can automatically complete these calculations is a smart move because it will simplify the process for you.
Know the finer details of leave entitlements and public holidays
The health and wellbeing of your employee is dependent on them taking time off. They are able to return to the job with a clearer head and greater level of productivity after taking a vacation. If you are able to have an understanding of the many sorts of leaves and holidays as well as the rules that govern them, you will be able to more effectively manage leave for your team and keep them satisfied.
Annual leave
Employees are permitted to take time off during the year for vacation, relaxation, or other personal reasons. When an employee is eligible for annual leave, eligibility is contingent upon meeting certain conditions; the minimum number of annual leave days that an employee is entitled to be determined by the law governing employment. You have the option, as an employer, of providing your staff members with additional annual leave days above and above the mandatory amount.
The rate of pay for yearly leave is often calculated based on a daily rate, however, this might vary depending on other regulations that are mandated by employment legislation.
Sick leave
If an employee is injured or ill, or if they need to care for a dependent who is injured or sick, they are permitted to take time off for sick leave. You are required by law to provide your employees with a certain number of sick leave days, but you have the option of providing them with additional leave as an additional benefit. The daily pay rate will be used to calculate sick leave compensation.
Public holidays
Workers are permitted to take unpaid time off on public holidays, as this type of time off is deemed to be equivalent to paid leave. If employees are compelled to work on holidays recognised by the government, you are obligated to pay them at the rate specified by statute (which may be different from their daily pay).
Other types of leave
Other sorts of leave, such as bereavement leave, parental leave, jury duty leave, and possibly even more types of leave, may be available to employees. They may also request unpaid leave, and it is up to you, as the employer, to decide whether or not to grant this request. Take into account the reasons given by your employee, and debate the best course of action with them.
Maintain a record of your employees’ time off work that is both accurate and up to date. A reliable payroll system will take care of that for you.
Health and safety responsibilities of employers
A significant part of your responsibility as an employer is to ensure that your staff members are both healthy and safe while they are on the job. Your employees will be more productive, the danger of illness and injury at work will be reduced, and you will be better able to comply with rules governing workplace health and safety if you establish a safe working environment.
Workplace health and safety practices
Put reasonable procedures into place to ensure the health and safety of your personnel, and then do all in your power to fulfil those procedures. Practices that contribute to workplace health and safety include the following:
- ensuring that an appropriate working environment and facilities are both maintained and provided for employees
- ensuring the presence of risk-free working conditions
- ensuring the safe handling, storage, and utilisation of resources at work
- providing staff with information and training on health and safety issues in the workplace
- ensuring the well-being and protection of your workforce at all times
Five questions to ask about the health and safety of your workplace
You have a responsibility to take care of your employees and fulfil your duties as an employer, and one way to do this is to be aware of the potential dangers that could arise in the workplace. Consider your answers to the following five questions regarding your place of employment:
- What kinds of health and safety hazards exist at my place of business, especially those that could put my employees at risk of getting hurt or sick?
- What are the potential consequences of these hazards, and how severe could they be?
- What are the chances that any of these dangers will materialise?
- How can I avoid these potential consequences?
- If I can’t get rid of them entirely, what other options do I have to reduce their impact?
Workplace health and safety in action
After you have determined the answers to the questions regarding the health and safety of the workplace, it is time to put into action the preventative measures that will lower the risks. The following are some examples of health and safety precautions that can be used in the workplace:
- a tutorial about workplace health and safety were given to new employees on their first day
- a forum through which workers can voice any issues they may have regarding the health and safety of the workplace and make suggestions for improvements
- a routine inspection of the safety equipment used in the workplace
- instruction for your staff members on how to use it
- a strategy for the safe evacuation of the workplace as well as for instructions on what to do in the event of an emergency
- workplace insurance for your employees (if this is within your budget)
In addition to this, it is recommended that you get in touch with a health and safety expert. They are able to assist with workplace plans, the establishment of accident registers, as well as the identification of hazards.
Protect the privacy of your employees
Keeping the personal information of your staff members safe and secure is an additional responsibility that you as an employer have. If you want to maintain any sensitive data on your employee, you will need their permission to do so. Because of this, you should avoid storing information about your employee that you do not require if it is not relevant.
If a worker asks for a copy of the information you keep about them, you should make sure to give it to them as quickly as you can after receiving their request. Avoid providing employee information to those who are not authorised to see it, and utilise employee information solely for purposes related to the work.
Chapter 6: Get started with employee forms and onboarding
It’s time to start the onboarding process with your new employee now that they’ve been recruited. We have some helpful checklists that will make the process of onboarding new employees a snap.
It is essential that a positive first impression be made on any new employee when they are being brought on board. You only have one shot at getting things right, so you should make the most of it.
It is critical to have an effective employee onboarding strategy in place if you want to engage your new staff and acquire their commitment right away. It makes a new employee feel more valued and at home as a member of your company when you do this.
Onboarding new employees entail more than simply conducting inductions and orientations. In order for employees to perform to the best of their abilities, it is necessary to set expectations, build relationships, and provide assistance.
Employee onboarding is made easy with these checklists
Working through a long list of to-do things is often necessary in order to successfully onboard a new employee. To make the process simpler for you, we have compiled a few helpful checklists that you can refer to.
Top tips for a great employee onboarding experience
The importance of providing a positive experience for new hires cannot be overstated. Here are five suggestions that will help ensure that your new employee is successful right from the start:
- Start early: Check that everything is in order before the first day of work for your new employee.
- Clarity is key: Give them a detailed plan outlining the steps they need to do in order to be successful in their profession.
- Constant communication: Make sure they are aware that you are always accessible to respond to any queries, provide a helping hand, or even just for a conversation in a more relaxed setting.
- Make it personal: Your new employee will have a better impression of their importance to the company if the onboarding process includes some personal touches.
- The little things count: Your new employee will have a better chance of succeeding if you provide them with all of the information they require, ranging from the location of the lunch area to instructions on how to operate the printer.
Chapter 7: Run payroll for your employees
Do you ever feel confused about how to handle the payroll for your employees? We walk you through the steps of the payroll process, explaining each step in detail so that you can perform it accurately.
Run payroll for your employees
Accurately processing payroll is a need. It is essential to maintain a productive connection with your employees by paying them on time and at the rate that was agreed upon. It’s also a legal obligation. Let’s take a look at the steps involved in processing payroll.
First, what is payroll?
A payroll is a list of all of an employer’s employees together with the total amount of money that is paid to those employees. It incorporates remuneration in the form of salaries or wages, as well as bonuses, allowances, and benefits. Payroll also includes deductions, such as taxes and social security.
Four ways to run payroll for employees
The processing of payroll for employees can take many various forms, and each of these forms has both advantages and disadvantages. Managing payroll for employees can be done in one of the following four ways:
- Spreadsheets or pen and paper: Payroll is handled by many smaller companies with less than five employees using either a straightforward spreadsheet or pen and paper. It does not cost anything, but the more employees you recruit, the more time you will spend managing it. You’ll need to educate yourself on the most recent tax legislation in order to avoid breaking the law and incurring the wrath of the ATO. When it comes to filing salary reports with tax offices that require electronic filing, this can also be an inconvenient process for some people. Under the Single Touch Payroll (STP) programme, you are required to disclose to the ATO on each payroll how much money was paid to your employees, how much tax was withheld, and how much money was contributed to their superannuation accounts. This report must be submitted using accounting or payroll software, a registered agent, or a payroll service provider. Alternatively, it can be submitted manually. If you keep your data on spreadsheets or write it down by hand, you will need to find a provider that will transform the information into a digital report format that is acceptable and then submit it on your behalf.
- Outsource to a specialist
You have the option of employing a specialist in payroll to carry out the work. They are well-versed in all aspects of taxation and will provide assistance to ensure that your obligations are met. Using a consultant will cost you money, and you will need to communicate often about employee changes; but, many businesses are willing to pay for the peace of mind that comes with using a consultant. - DIY software
There are a lot of different software packages that can conduct the calculations and some of the administrative work for you. For instance, they will compute the amount of back pay you are owed in addition to the necessary deductions, generate paystubs, and automatically fill out tax forms. However, the responsibility for actually making the payments is with you. - Full-service software
You can subscribe to systems that perform all of the tasks that DIY software does, in addition to allowing you to make payments and submit reports. The vast majority of the remaining tasks have already been completed for you; nevertheless, you will be required to add personnel to the system and modify their profiles if necessary.
A reliable payroll system simplifies the complications, assists you in avoiding errors that may lead to expensive penalties, and handles all of the hard work on its own, allowing you to direct your attention to other aspects of your organisation. Pick a way of handling payroll that works well for you and satisfies the requirements of your company.
When to run payroll
When it comes to the timing of payday, there are a lot of traditions and customs. It occurs on a Wednesday or a Thursday in Australia the vast majority of the time. And workers are typically compensated once per week, twice per month, or once per month.
The frequency with which employers pay:
- 28% weekly
- 52% fortnightly
- 15% monthly
- 5% other
According to one quarter of workers, the pay cycle makes it difficult for them to budget and save money. It is an area in which small firms can distinguish out from the competition by assisting workers in accomplishing their monetary objectives.
How frequently employees would like to get paid:
- 46% weekly
- 39% fortnightly
- 9% monthly
- 5% other
* Xero Australian workforce survey, 2019
How to run payroll – from start to finish
The process of calculating payroll often becomes convoluted since there are so many phases involved. We will walk you through the procedure step by step so that you can correctly process payroll.
1. Prepare for payroll
You might consider opening a separate bank account for your payroll if you want to maintain track of your business activities in a manner that is distinct from your payroll transactions. Paying your employees and storing funds for taxes, deductions, and other payroll-related expenses will both be handled through the bank account that you have designated as your payroll account. When paying staff, you might need to set up direct deposits with your bank so that the money goes directly into their accounts (if this is the method of payment you agreed on).
Before you pay a new employee, you will likewise be required to submit certain documents. For further information on this topic, please refer to the chapter that is focused on the process of onboarding employees.
2. Calculate employee pay
You are responsible for determining the total gross pay for each of your staff members. The complete amount of money that is owed to an employee for the pay period according to the terms of their contract is referred to as the employee’s gross pay. In addition to that, it incorporates holiday pay and payment for overtime worked on public holidays. The employees won’t actually receive their full gross compensation because deductions will be taken out before they are paid. This is something that, with the right payroll software, can be done automatically. If you have wage workers, it will even take care of the requests for time off and the time sheets.
3. Calculate pre-tax deductions
Deductions taken out of an employee’s paycheck are referred to as payroll deductions. While others are entirely up to the individual, others are mandated by law. When you make a deduction, it is your responsibility to ensure that the money is sent to the appropriate recipient, whether that recipient is a governmental body or a retirement fund. While some deductions are taken out of an employee’s paycheck before taxes are deducted, others are taken out of the paycheck after taxes have been deducted.
Among the things that qualify for deductions before taxes are:
Superannuation (super)
A significant obligation for employers is the provision of retirement benefits for their workforce. They are required to do it, and it contributes to their retirement savings. Your payments will not come out of the wages or salaries of your employees; rather, they will come out of the expenditure account for your company.
- When an employee’s compensation reaches a specific threshold, you are required to begin making contributions to their retirement fund.
- The contribution rate is around 9.5% of the total earnings of the employees.
- If your employee doesn’t nominate a super fund, you’ll pay into a default fund.
4. Calculate employee-related taxes
At the end of each pay period, you are responsible for deducting taxes from the wages of your employees and calculating the amount of payroll taxes that you owe as an employer. It’s possible that, before turning these taxes over to the government, you’ll first need to keep hold of them for a little while. It might be smart to open a separate bank account just for them at the bank.
PAYG (pay-as-you-go income tax)
This is the amount that will be taxed on the wages of your employee. This includes a levy that is paid to Medicare and also takes into account the tax-free maximum, tax offsets, and repayment of student loans. Check out the page on PAYG withholding that’s been provided by the ATO. You can also use some tax tables and an online tax withholding calculator that the ATO provides for you to determine how much PAYG tax should be deducted from your paycheck.
Taxes on benefits
Your employees are expected to pay tax on allowances, bonuses, and fringe benefits such as housing or private use of a company car. Check out the ATO pages on allowances, withholding for allowances, and fringe benefits tax, as well as the ATO tax table for back payments, commissions, bonuses, and similar payments.
Payroll taxes
Your business may face extra state or territory taxes if you pay a lot in salary and wages. Check out the ATO page on paying payroll tax and the Payroll Tax Australia website.
5. Calculate post-tax deductions
Your employee may have extra deductions to come out after tax. Child support is one of the most common. Check out this Department of Human Services page on child support information for employers.
6. Make payments to employees
When calculating your employees’ nett compensation, you must first deduct all taxes and deductions from their gross pay. After you have determined their final nett salary, it is time to pay them. Pay according to the mode of payment that you and the other party have agreed upon. Make sure that your employees receive payslips on a regular basis. On their paystub, you will see not only their gross pay but also the deductions that were deducted from it as well as the amount of their nett pay.
Good payroll software automatically looks after all the calculations for you, processes payments on time, and makes it easy for employees to view their payslips. If you don’t use payroll software, a payslip template can be useful.
7. File and pay taxes, deductions, and contributions
After you have computed all of the applicable taxes, deductions, and contributions, it is time to file your return and make the necessary payments. You must complete it before the deadline in order to avoid incurring any fines or interest charges.
Each time payroll is processed, the majority of companies are required to provide the ATO with a report detailing what employees were paid, how much tax was withheld, and what superannuation contributions were made.
8. Keep payroll records
Record-keeping is the very last stage of the payroll procedure that you have reached at this point. You need to make sure that you retain payroll records in case there are any questions. You’ll need to retain records, either in physical or digital form, for the following reasons:
- salary or wages and time worked
- holidays and leave
- taxes and other deductions
- employer contributions
- when money was paid and where to for employee pay
You must keep these records for at least seven years, even if your employee has left.
For more information, visit the Fair Work Ombudsman page on record-keeping.
Chapter 8: Manage employee evaluations
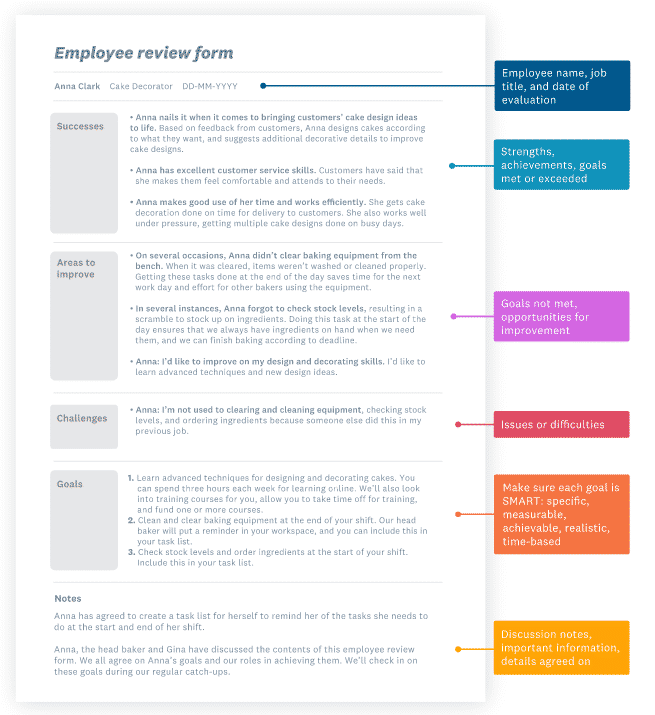
(Credit: Xero.com)
Employees contribute to the expansion of your company, but they also require support from you. The following is a guide for doing employee assessments in order to get the most out of your team.
When you run a small business, it’s always nice to know that you have the support of one or two employees, if not a full team. You can rely on them to help things operate smoothly and to provide support as you build your company.
However, your staff members also require your assistance. They need to know if they are progressing in the right direction towards accomplishing the objectives that you outlined for them at the beginning of the process. They also need to be aware of the things that they are doing well as well as the areas in which they may make improvements. Evaluations of staff members are of use in this regard.
What is an employee evaluation?
An employee evaluation, which may also be referred to as an employee performance review or employee appraisal, is a method through which you can examine the performance of your employee. Evaluations of workers enable employers to coax the best performance out of their staff members by providing constructive criticism regarding areas in which workers excelled as well as those in which they may improve.
Your employees will likely remain with your company for a longer period of time if you have a decent procedure for evaluating their performance. This is because they will feel happier and more secure in their jobs.
Why do employee evaluations matter?
Your staff are your most valuable investment. Your company will profit, and you will be able to accomplish more of your goals if you support them in their professional journey.
The following are some of the reasons why employee assessments are so important:
- to provide your staff with goals that are lucid and within their reach
- to determine whether or not the goals are being met or exceeded
- to discover the areas in which the personnel of the company can improve
- to keep a record of the performance and advancement of employees
- to take into consideration when determining wage increases or promotions
- to determine whether or not a person is happy in their employment and to learn about their professional aspirations
When to do employee evaluations
Evaluations of staff members are typically carried out on a yearly basis, either at the close of the calendar year or on the occasion of an employee’s work anniversary. However, it is recommended that you carry out this task on a more regular basis, perhaps once every two months or once every quarter. It is preferable to meet with employees only once or twice a year to provide input on their performance as opposed to providing continuous feedback on their work.
Check in with your staff members once a week, twice a month, or once a month. Discuss what it is that they are working on at the moment and address any problems or difficulties that they are encountering. Your staff will have the opportunity to share their thoughts and opinions regarding your company during these ongoing conversations.
Employee evaluation in action
So how exactly does one evaluate a worker’s performance? It is a process that never ends and requires a lot of introspection as well as cautious judgement. The key is to pay attention and offer criticism in a constructive manner. Rather than fixating on errors of the past, the focus should be on providing opportunities for individuals to advance in their current roles.
When conducting employee evaluations, the following steps are required.
Be prepared
Making an appointment for each employee review in advance ensures that both you and the employee have sufficient time to prepare for the event. If you want your employee to feel at ease, reserve a quiet spot within your company or have the meeting in a location with a more laid-back atmosphere, such as a coffee shop.
Examine the employee’s job description as well as the notes you’ve taken throughout the regular check-ins you’ve been conducting in order to get ready for the evaluation. Collect information on your employee from their manager, their peers, and even customers they’ve worked with in the past.
You may organise your thoughts with the help of this sample employee review form by using it:
Request that the employee complete the employee review form in advance so that they can make an evaluation of their own performance.
When filling out the form, it is important to be as specific as you can. Include real instances and exact details if you can. Therefore, as an accomplishment, rather than listing something generic such as “Delivers on time or even earlier,” write in “For project X, Jess delivered the design document three days earlier than the required date,” rather than “Delivers on time or even earlier.” Because of this, the production team got to work right away on the drawings, and they were able to hand in the finished product one day ahead of the deadline.
Encourage a two-way conversation
Make use of the employee evaluation form as a place of departure. When discussing employee performance, it is important to remember that it is a conversation that goes in both directions; therefore, you should urge your employee to express their perspective. Inquire about their thoughts and opinions on the following topics:
- Successes: To what extent are they successful in the various aspects of their jobs? What do you consider to be their most significant accomplishments to date?
- Improvements: What are some of the areas in which they could make improvements? What should they be making their top priority? Where should their attention be placed? What needs to be different in order for them to have better results?
- Challenges: What aspects of their employment do they find to be the most difficult? What other challenges do they need to overcome? In what ways can you assist them in overcoming these challenges or problems (such as by giving training or other types of equipment)?
- Job satisfaction: Are they happy with their job? Do they want to take on new challenges or additional responsibilities? Are they struggling with work-life balance?
It is also the right moment to have an open and honest conversation regarding wages and advancement opportunities. Have a conversation with your staff members about potential wage raises, bonuses, and how they can advance to other roles or positions in the company.
Outline future goals
Your employee should have goals that are attainable, and you should let them have some input on what those goals should be. Collaborate with them to determine the most effective means of accomplishing those objectives. During each employee review, you should go back and revise their goals, and when you have your regular catch-ups with the employee, you should check in with them to make sure they are still on pace to achieve those goals.
Document the discussion
Take notes during the conversation, and make sure to record everything that has been decided upon. Give these notes and the accompanying materials to your employee so that they may be reminded of their objectives, and also so that you can be reminded of what you need to do to assist them. You will also make use of them as a basis for the subsequent employee review that you conduct.
Five tips for more effective employee evaluations
Your staff will be able to perform to their full potential if you use evaluations effectively. The following are five suggestions that will help you make the most of employee performance reviews:
- Give constructive feedback
Recognize the efforts of your employees and direct your attention to how they might improve. Provide them with feedback that may be acted on and guide them to the information that they need. - Be objective
When evaluating employees, you should make every effort to eliminate any bias. Instead of focusing on a single mistake they made in the past or a recent accomplishment, shift your attention to the bigger picture of their performance. - Explain why employee evaluation matters
Spend some time explaining to your workers why you are doing performance reviews and give them the opportunity to ask questions. Give them an explanation as to why it is important to you that they do a good job and what the consequences will be for your company if they don’t. - Don’t catch them off guard
Avoid bringing up any concerns during the employment evaluation by not waiting until then. Bring them up as soon as problems occur so that you and your employee may begin working on a solution as soon as possible. - Show your appreciation
You should express gratitude to your employee for whatever they’ve done that exceeds your expectations and thank them for it. Reward them for their success, even if it’s something as simple as a thank-you message, buying them a cup of tea, or mentioning them at your next team meeting. Even if it’s something as simple as a thank-you note or buying them a cup of tea, do something. A small amount of appropriately timed praise can go a long way.
Chapter 9: How to grow your team after the first few hires
The process of elevating your team from “zero to hero” is a difficult one. We have some advice and suggestions that will help you successfully expand your team, and we are here to assist you in reaching your goal.
Becoming an employer requires more than just recruiting new workers, orienting them, managing their salary, and evaluating their performance. It is also about being a good leader and putting together a strong group. However, putting together a group of people might be difficult. Every member of the team is unique, with their own set of experiences, personalities, as well as skills and weaknesses, that they bring to the table.
Eight ways to build a winning team
In order to construct a team that is capable of achieving its goals, you will need to instil in its members a strong sense of camaraderie, respect, and trust.
In addition to this, you will need to create a working atmosphere that encourages communication, collaboration, and creative thinking.
How exactly do you go about doing that? Creating a successful team can be accomplished in the following eight ways.
- Share your vision
The members of your team should be aware of the long-term objectives you have set for the company. Inform them of your goals and the plans you have in place to make them a reality, and share your vision with them. Give them an explanation of where you see your company going in the next few months and in the following few years, and how you see it getting there. After you have provided your team with an overview of the situation, it is time to focus on the specifics of the situation. Assist your staff members in comprehending how the functions of their roles assist to the realisation of your vision and how they fit into your plans. - Set team goals
Develop a set of team goals that are aligned with the overall objectives of the company. Your team will be better able to understand what they are working for, what their priorities are, and how to make decisions that are in line with the goals that they have set collectively as a result of this. Your team will also have a shared purpose as a result of these objectives, which will help to foster a sense of “us” rather than “them and me.” - Define clear roles and responsibilities
Make sure everyone on your team is aware of how the many jobs they play fit together. The obligations of each member of the team are dependent on one another, and these interdependencies are essential to the accomplishments of the group. For instance, a person delivering their goods late or failing to do a task that is required of them as part of their profession can result in disagreements and misunderstandings. Discuss with your team how their jobs are tied to one another and how each member of the team is dependent on the performance of the others in order for the team as a whole to succeed. - Build relationships with your employees
Invest some time in getting to know each member of your team better, including their specific skills, the areas in which they excel and struggle, as well as the things that they like and avoid. When you have a deeper understanding of them, you will be able to motivate them better. You are able to connect their skills to specific jobs and determine which challenges they are most suited to address. Learn about your staff members in other contexts besides the office. Inquire with them about the things that they enjoy doing in their spare time. It’s a nice way to show your staff that you care about them on a personal level. - Show your employees that you value them, Recognize the hard work that your staff has put in and thank them for it. Celebrate their accomplishments by taking them out to lunch as a group, presenting them with a gift card or voucher for the takeout restaurant of their choice, or highlighting them on the website and social media accounts of your company. Be sincere in expressing your gratitude for whatever it is that was done for you. Offering bonuses to one’s workforce is yet another strategy that can be utilised to boost morale and maintain satisfaction levels. This may take the shape of monetary rewards for outstanding performance, the provision of fresh tools or a hip new attire, or even the assumption of the financial burden of training sessions designed to enhance their capabilities.
- Embrace diversity
The diversity of the team’s members is one of the group’s greatest assets. You will find the finest solution by considering contrasting points of view; therefore, maintain an open mind to alternative ideas and methods of tackling the problem. You can stimulate creativity and innovation on your team by appreciating the unique contributions that each member brings. - Be a good leader
For a team to be effective, its leader must also be effective. Respect each person of your team while maintaining your authority while remaining approachable, fair, and committed to keeping your word. You might not have much experience managing people or leading teams, so it would be smart to invest in yourself by attending some classes on leadership and management. It’s an ongoing educational experience, and as you go along, you’ll find strategies that are effective for your particular situation. - Do fun team-building activities
Participating in activities as a group can assist generate shared experiences and facilitate the development of positive working relationships. These activities help your team create trust in one another, improve communication, and work more efficiently as a unit. Check your finances to determine what you are able to spend. Activities that are meant to create teams might be as uncomplicated as going out for drinks on a Friday night after work, or they can be as involved as hosting monthly game evenings, movie nights, or quiz nights. You should put some work into it, but you should also remember to take some time to rest, unwind, and enjoy yourself.
